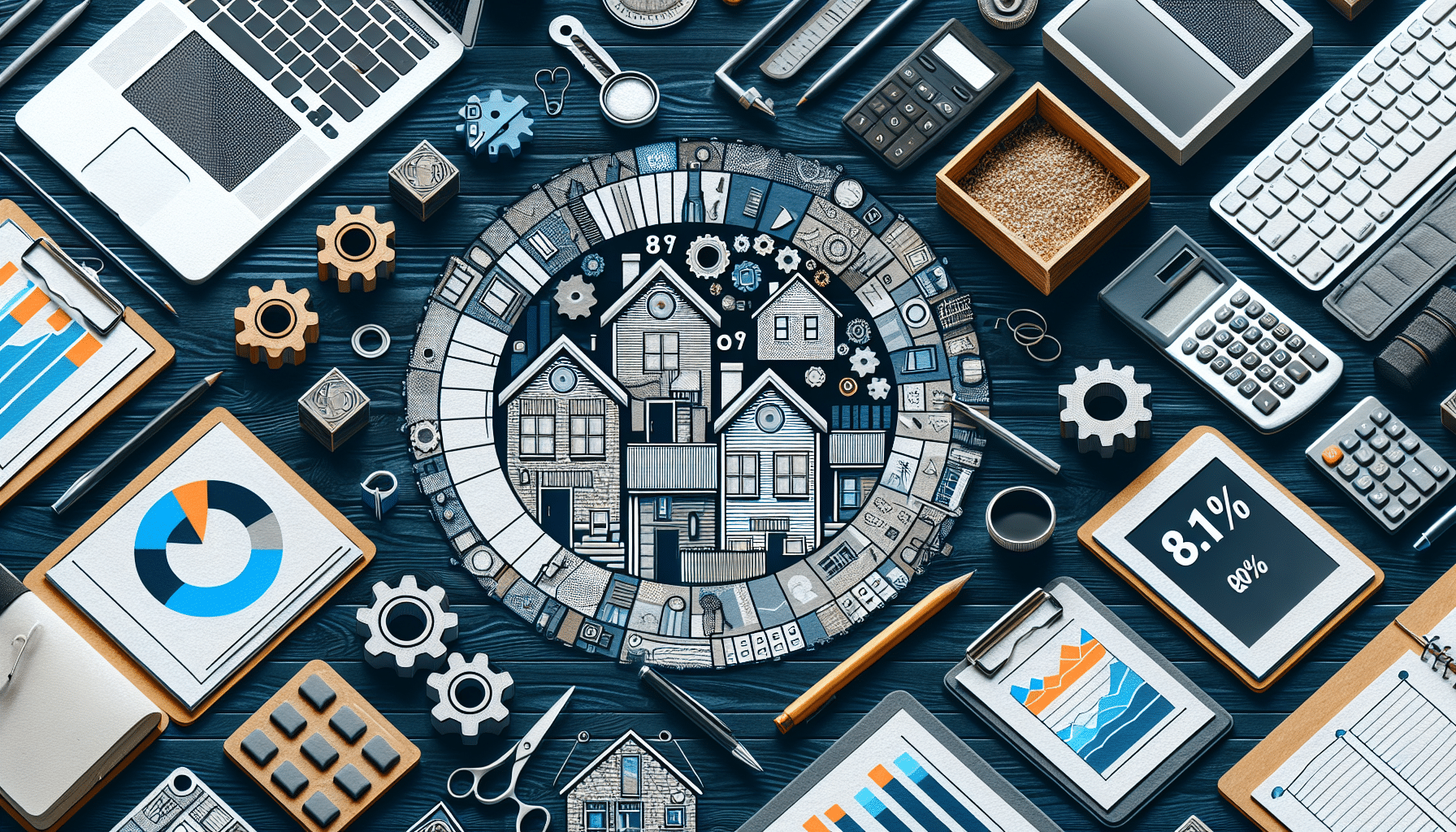
In 2023, it has been reported that 8.1% of people under 65 years old in the European Union live in households with very low work intensity. This situation is defined by the fact that the working-age members of these households only worked up to 20% of their total possible working hours in the previous year, raising serious concerns about the employment and economic well-being of these families.
Among the regions with the highest percentages of people in this situation, France stands out. In Guyane, an alarming 41.7% of the population is in households with very low work intensity, followed by La Réunion with 22.5%. Germany also presents worrying figures; for example, in Bremen, 21.8% of the young population faces this reality. Additionally, other regions such as Hainaut in Belgium (21.5%) and Campania in Italy (21.2%) contribute to this issue.
On the other hand, the situation in certain areas of Europe is notably more favorable. The region of Bucureşti-Ilfov in Romania has the lowest record, with only 0.7% of its population in households with very low work intensity. Other Austrian regions, such as Salzburg (0.8%) and Tyrol (1.1%), also report significant figures below the average. Additionally, Bratislavský kraj in Slovakia with 1.3% and the Nord-Est region in Romania, with 1.7%, join the areas with better indicators.
These data underline the marked regional disparities within the European Union, highlighting the urgent need to implement specific interventions that address job insecurity and promote economic stability in the most affected regions. The comparison between different areas reveals that labor well-being is not homogeneous and that numerous factors influence the work capacity of European citizens, highlighting inequality in access to job opportunities.
Referrer: MiMub in Spanish