Here’s the translation into American English:
—
A new approach to generative artificial intelligence is emerging thanks to the use of multi-agent systems, which leverage the collaboration of multiple specialized AI agents to tackle complex tasks that exceed the capacity of a single model. By combining agents with different skills, such as language, vision, and audio, these systems can work either in parallel or sequentially, producing more robust results. Recent research suggests that collaboration among several agents can increase success rates in complex tasks by up to 70% compared to methods that use a single agent.
However, implementing these systems poses significant challenges in terms of computational demand. Modern applications often generate thousands of prompts for each user query, necessitating high performance in data processing. In this context, Amazon Nova stands out for its high processing capacity, achieving more than 200 tokens per second with minimal latency in response generation. This efficiency, along with affordable costs, allows teams to effectively manage the large number of actions required by multi-agent intelligence.
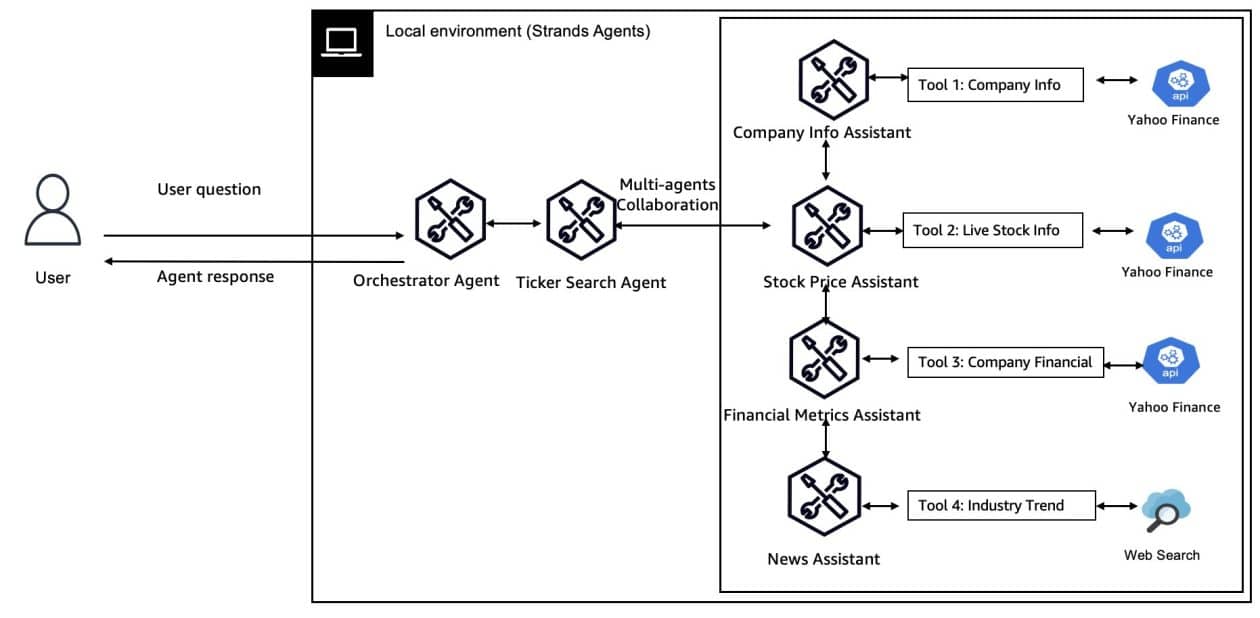
Multi-agent systems can be designed using different collaboration patterns, each with specific advantages depending on the type of task at hand. For example, the “agents as tools” pattern allows a main agent to delegate tasks to expert sub-agents, optimizing the accuracy and complexity of responses. This approach is ideal for queries broken down into distinct subtasks, such as travel planning, where different agents can handle different aspects of the request.
Another pattern, the “swarm,” focuses on decentralized collaboration among a group of agents working toward a common goal, allowing for unique contributions that can lead to more innovative solutions. Meanwhile, the “structured graph” pattern helps developers define clear connections between agents, ensuring a directed and controlled flow of information, which is beneficial in complex decision-making processes.
Finally, the “workflow” pattern aims at orchestrating multiple agents in predefined sequences, facilitating precise management of dependencies and the order of execution. This approach is particularly advantageous in situations requiring a clear process to be followed, such as content generation and data analysis.
In conclusion, multi-agent systems represent a significant advancement in generative artificial intelligence, promising not only to improve efficiency in solving complex tasks but also to optimize costs and processing times thanks to innovations such as Amazon Nova. The adoption of these design patterns opens the door to applications that can evolve from simple prototypes to robust production architectures.
Referrer: MiMub in Spanish