Generative artificial intelligence has emerged as a key factor in transforming the healthcare sector, opening new opportunities to improve care management and patient engagement. This technology, which enables clinicians to provide more efficient care through automated systems and diagnostic support tools, has been the subject of a recent revealing study. The analysis indicates that medical students who received feedback generated by large language models (LLMs) during clinical simulations showed a significant improvement in their decision-making compared to those who did not have access to this tool.
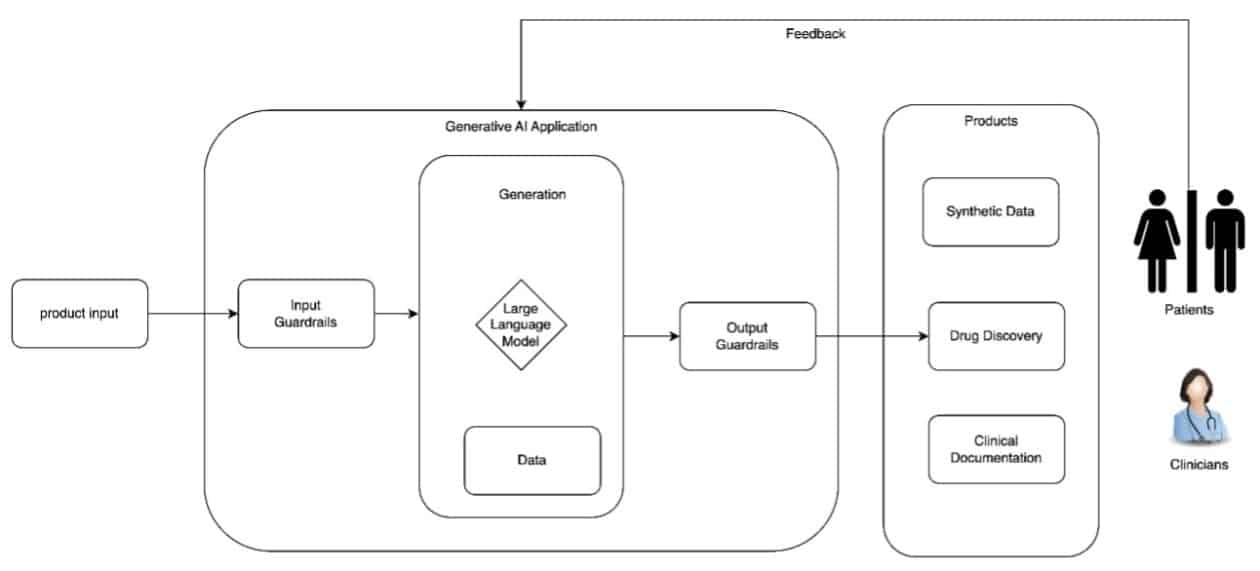
Large language models are fundamental to most generative AI systems, as they facilitate natural and effective interactions. This capability translates into the creation of solutions across various areas, from billing to medical diagnosis and treatment, allowing these technologies to operate autonomously under human supervision. However, their implementation is not without challenges; a deep understanding of the associated risks is required, along with the need to establish a comprehensive approach that ensures the safe and responsible development of generative AI applications.
In the process of designing these applications, it is essential to define policies that regulate the inputs and outputs of the systems. These guidelines are crucial for ensuring a responsible approach to their development. Additionally, it is important to consider potential risks, such as confabulation—where the model may generate incorrect responses that seem accurate—and inherent bias, which can exacerbate inequalities among different segments of the population.
Transparency is another essential pillar in the lifecycle of generative AI applications. Documenting data sources, design decisions, and limitations is fundamental to facilitating system evaluation and empowering end users in their decision-making. Additionally, best security practices should be integrated at every level of development, safeguarding both patient privacy and data security. Given that these applications may be susceptible to adversarial attacks, it is advisable to conduct risk assessments and establish appropriate protective measures.
In summary, generative artificial intelligence offers significant potential to improve healthcare through optimizing service, enhancing patient experience, and ensuring clinical safety. When designing and operating AI applications, it is crucial to systematically address limitations and create a governance framework that ensures the safety and trust that users demand.
Referrer: MiMub in Spanish